CNN#
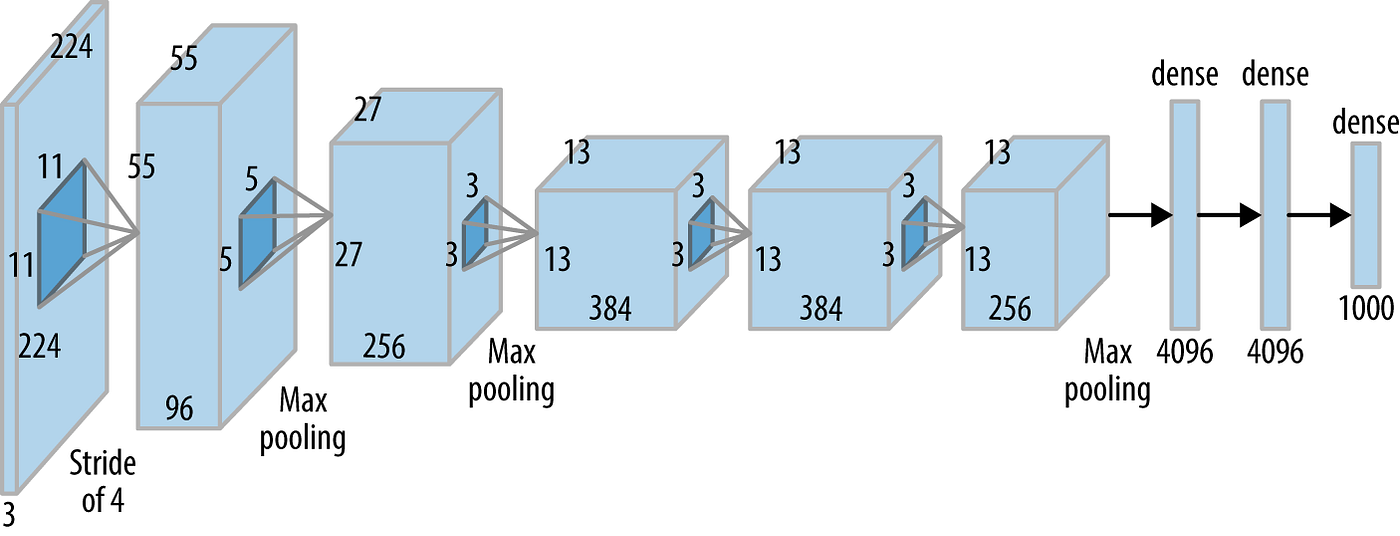
One of the pioneering deep convolution neural networks (CNN) AlexNet won the ImageNet Large Scale Visual Recognition Challenge (ILSVRC) in 2012. This event is now accepted as a key point of beginning of the deep learning era.
CNN vs MLP#
In CNN new kind of layers are introduced such as convolution and pooling. Why are they important for image processing?
An image in ImageNet collection usually has shape \(224\times 224\), and it has three channels: red, green and blue. Hence, such image can be considered as a vector of size \(224\times 224 \times 3 = 150528\).
Question
Suppose that we are applying a linear layer to this vector, and the output has the same shape. How many parameters does such dense layer have?
Answer
The matrix of weights will conatain
So, the number of parameters becomes too big. An MLP with so many parameters will train for a quite long time, and it could be easily overfitted. On the other hand, a convolution layer has much less parameters. For example, it the kernel size is \(11\), number of input and output channels is \(3\), then there are
weights in the convolution layer.
Advantages of convolutions#
Local Connectivity. Convolutional layers have local connectivity, meaning each neuron is connected to a small local region of the input, enabling them to focus on local features and patterns.
Parameter Sharing. Convolutional layers use parameter sharing, where the same set of weights (filter) is applied to different parts of the input. This reduces the number of parameters, making the network more efficient and less prone to overfitting.
Translation Invariance. Convolutional layers inherently exhibit translation invariance, meaning they can recognize patterns regardless of their exact position in the input. This is particularly valuable for tasks like image recognition.
Parameter Efficiency. Convolutional layers are parameter-efficient compared to fully connected layers, especially when dealing with high-dimensional input data like images. This efficiency is crucial for training deep networks.
Efficient GPU Implementation. Convolutional operations can be highly parallelized, making them well-suited for efficient GPU implementation. This parallelization enhances the speed of both training and inference.
